In accounting, the method of recording financial transactions can be broadly categorized into Single Entry and Double Entry bookkeeping systems. Both of these systems are essential for maintaining financial records, and they differ in how transactions are recorded and analyzed.
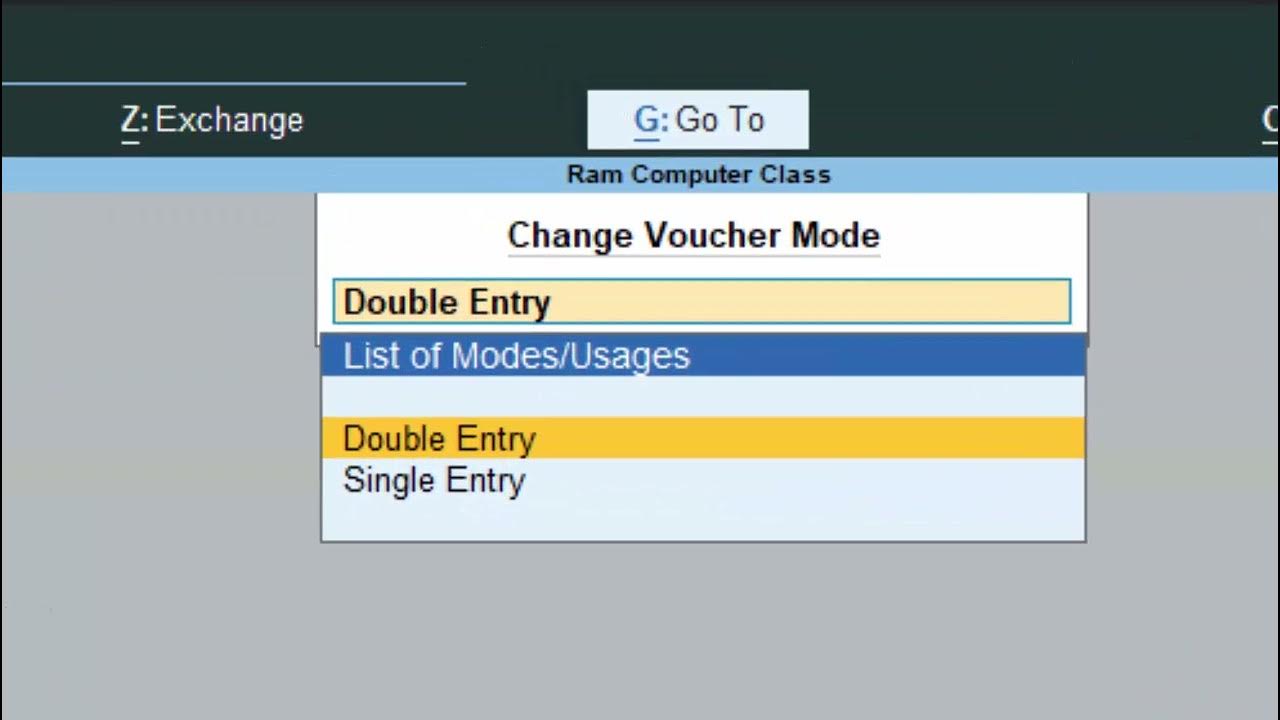
What is Single Entry Mode?
Single Entry bookkeeping is a simple method of accounting where each financial transaction is recorded only once, either as income or expense. In this method, only the debit side is recorded, and there is no formal system to balance the credit side.
Advantages of Single Entry:
Simple and easy to maintain.
Suitable for small businesses.
Low cost of implementation.
Disadvantages of Single Entry:
Does not provide a complete picture of financial health.
It is not as accurate or reliable as Double Entry.
How to Use Single Entry Mode in TallyPrime?
- Open TallyPrime and select your company.
- Go to Gateway of Tally → Vouchers.
- Select Payment (F5), Receipt (F6), or Contra (F4).
- Enter the transaction details (e.g., amount, party, bank/cash account).
- Press Enter to save the transaction.
What is Double Entry Mode?
Double Entry bookkeeping is a more advanced and widely accepted accounting system where every financial transaction is recorded in two accounts: one is debited, and the other is credited. This method follows the standard accounting principles of debit and credit and based on the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity), ensuring that the debits always equal the credits.
Advantages of Double Entry:
- Provides a complete and accurate picture of financial transactions.
- Helps maintain the accounting equation.
- It is more reliable and accepted by businesses, banks, and auditors.
Disadvantages of Double Entry:
- Requires more effort and expertise.
- More complex than Single Entry.
How to Making Single Entries and Double Entry?
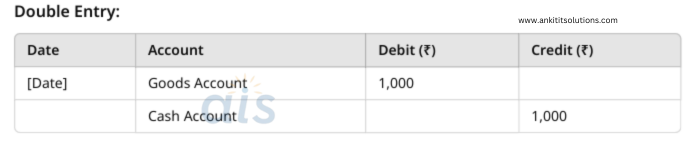
1. Purchased goods worth ₹1,000 in cash.
Single Entry:
- Debit: Goods Account (₹1,000)
- Cash Account: Reduce cash by ₹1,000
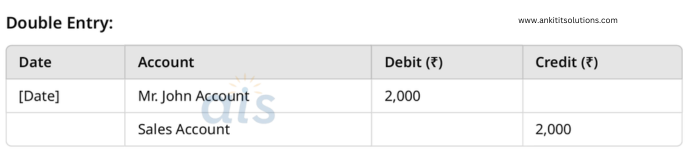
2. Sold goods worth ₹2,000 on credit to Mr. John.
Single Entry:
- Credit: Sales Account (₹2,000)
- Accounts Receivable: Increase by ₹2,000
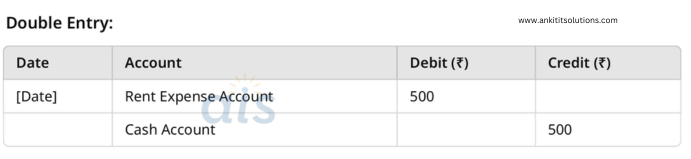
3. Paid rent of ₹500 in cash.
Single Entry:
- Debit: Rent Expense Account (₹500)
- Cash Account: Reduce cash by ₹500
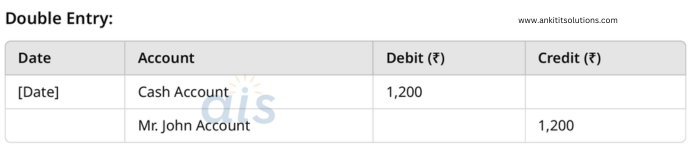
4. Received ₹1,200 from Mr. John.
Single Entry:
- Credit: Accounts Receivable (₹1,200)
- Debit: Cash Account (₹1,200)
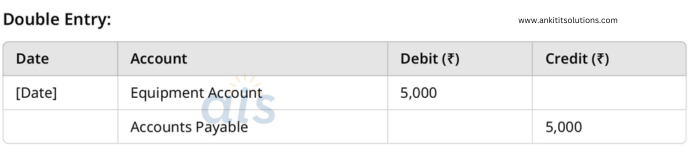
5. Purchased equipment worth ₹5,000 on credit.
Single Entry:
- Debit: Equipment Account (₹5,000)
- Accounts Payable: Increase by ₹5,000
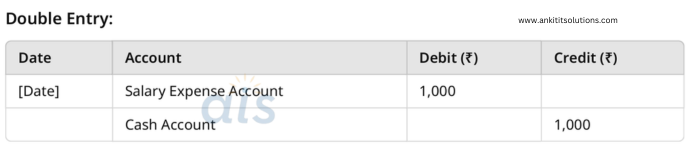
6. Paid salaries of ₹1,000 in cash.
Single Entry:
- Debit: Salary Expense Account (₹1,000)
- Cash Account: Reduce cash by ₹1,000
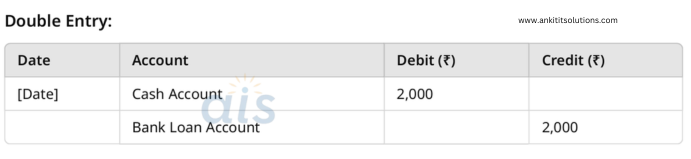
7. Borrowed ₹2,000 from the bank.
Single Entry:
- Credit: Loan Payable Account (₹2,000)
- Debit: Cash Account (₹2,000)
8. Sold goods worth ₹1,500 for cash.
Single Entry:
- Credit: Sales Account (₹1,500)
- Debit: Cash Account (₹1,500)
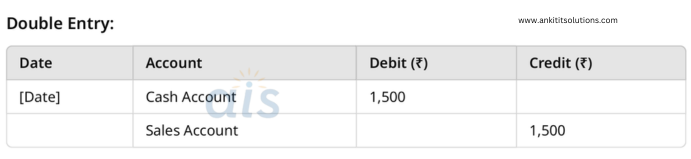
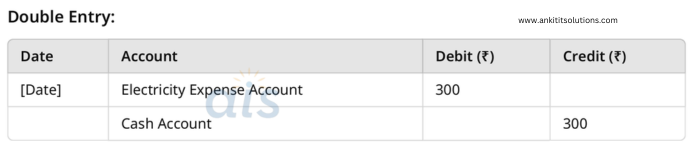
9. Paid ₹300 for electricity bill in cash.
Single Entry:
- Debit: Electricity Expense (₹300)
- Cash Account: Reduce cash by ₹300
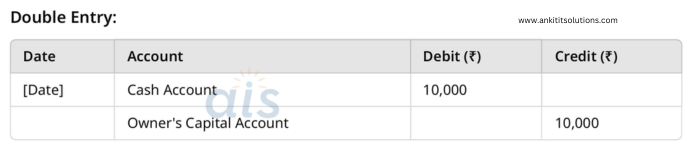
10. Owner invested ₹10,000 in the business.
Single Entry:
- Debit: Cash Account (₹10,000)
- Capital Account: Increase by ₹10,000
Both Single Entry and Double Entry bookkeeping systems serve the purpose of recording financial transactions, but the latter is more comprehensive and accurate. While Single Entry is easier to maintain and suitable for small businesses, Double Entry provides a complete and balanced record of financial activities. TallyPrime simplifies both systems, especially Double Entry, by automating calculations and ensuring that the accounting equation stays balanced.